Although hydropower remains the world’s leading form of renewable energy, wind and solar capacity ramped up rapidly during 2012, according to a study just released by the Washington, DC-based Worldwatch Institute, an environmental research organization.
The market for green power continues to grow: Last year, solar power consumption increased by 58 percent to 93 terrawatt-hours (TWh), and the use of wind power increased by 18 percent to 521 TWh, according to the report, “Vital Signs Online.” Indeed, solar and wind continue to dominate in terms of dollars spent and are quickly becoming the highest-profile renewable energy sources.
Investments Down, Growth Up
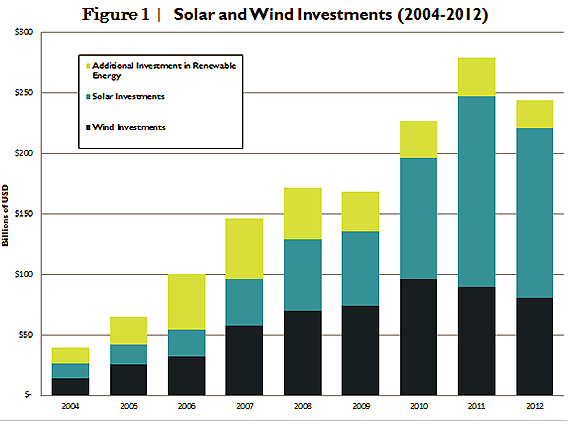
Interestingly enough, global solar and wind energy capacities continued to escalate—even while new investments in these energy sources declined during 2012. Global investment in solar energy reached a cumulative $140.4 billion, an 11 percent decline from 2011, and wind investment was down 10 percent, to $80.3 billion.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) installed capacity grew by 41 percent in 2012, reaching 100 gigawatts (GW). Over the past five years alone, installed PV capacity has increased by 900 percent—vaulting up from a mere 10 GW in 2007. The countries with the most installed PV capacity today are Germany (32.4 GW), Italy (16.4 GW), the United States (7.2 GW), and China (7.0 GW).
During 2012, Europe remained dominant in solar, accounting for 76 percent of global solar power usage. Germany, alone, accounted for 30 percent of the world’s solar power consumption, and Italy added the third most capacity of any country (3.4 GW). Spain added the most concentrating solar thermal power capacity (950 megawatts). However, Italy reached the subsidy cap for its feed-in tariff (FIT) program in June 2013, while Spain recently made a retroactive change in its FIT policies—meaning growth in solar energy will likely slow in these countries in the near future.
Due to slowing global economic growth, easing demand, and oversupply, there were significant net losses in the Chinese PV industry, which supplies more than half of the world market. The net losses have been exacerbated by on-going solar trade complaints among China and both the European Union (EU) and the United States after these regions accused Chinese companies of dumping solar panels on their markets and providing illegal subsidies to its manufacturers. With fewer opportunities to export, China’s domestic capacity is likely to grow. The country’s 12th Five-Year Plan aims to reach 21 GW installed solar capacity by 2015 and 50 GW by 2020.
A Strong Wind Sector
Total installed wind capacity edged up in 2012 by 45 GW to a total of 284 GW, an 18.9 percent increase from 2011. In keeping with recent years, the majority of new installed capacity was concentrated in China and the United States, which reached total installed capacities of 75.3 GW and 60 GW respectively.
Indeed, the United States was the world’s top wind market in 2012. Overall capacity increased 28 percent as the nation added 13.1 GW—double the amount it added in 2011. Increased domestic manufacturing of wind turbine parts, improved technological efficiency, and lower costs helped spur this increase, but the greatest catalyst was the threat of expiration of the federal Production Tax Credit (PTC), which provides tax credits for kilowatt-hours produced by wind turbines, at the end of 2012. A slowdown was originally expected in 2013, but the U.S. Congress extended the PTC until the end of the year.
The EU remained a dominant region for wind power, as it passed an important milestone— installing 11.9 GW of new capacity to reach 106 GW, representing 37.5 percent of the world’s market. Currently, wind accounts for 11.4 percent of the EU’s total installed generation capacity. Germany and Spain remained Europe’s largest wind markets, increasing their total installed capacity to 31.3 GW and 22.8 GW, respectively. The United Kingdom was third in new installations in 2012, at 1.9 GW, followed by Italy with 1.3 GW.
Other Highlights
Among the other major findings of the report are the following:
- In 2012, installed capacity for concentrating solar thermal power (CSP (News
 - Alert)) reached 2.55 GW, with 970 megawatts (MW) added in 2012
- Alert)) reached 2.55 GW, with 970 megawatts (MW) added in 2012
- The Asia-Pacific region now accounts for 17 percent of global solar use, trailing behind only Europe
- Political instability continued to slow growth in Africa and the Middle East, but installed capacity grew by 9.3 percent in 2012 ,compared with 2011’s rate of 2.6 percent
“Although policy uncertainties and changes will likely challenge the growth of solar and wind in the future, these technologies are nonetheless well poised to grow,” said Worldwatch Sustainable Energy Lead Researcher Matt Lucky, who co-authored the report. “Declining solar technology prices, while challenging for current manufacturers, are helping solar to reach near grid-parity in many markets. With the decreasing cost of operating and maintaining wind farms, wind power is already cost competitive with conventional power energy sources in many markets.”
Edited by Blaise McNamee
 Internet Telephony Magazine
Click here to read latest issue
Internet Telephony Magazine
Click here to read latest issue CUSTOMER
CUSTOMER  Cloud Computing Magazine
Click here to read latest issue
Cloud Computing Magazine
Click here to read latest issue IoT EVOLUTION MAGAZINE
IoT EVOLUTION MAGAZINE